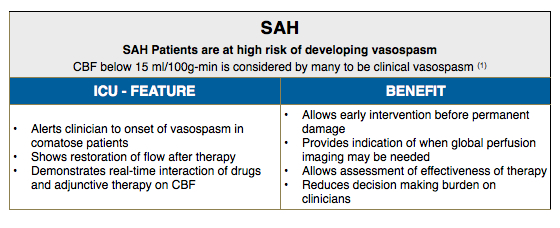
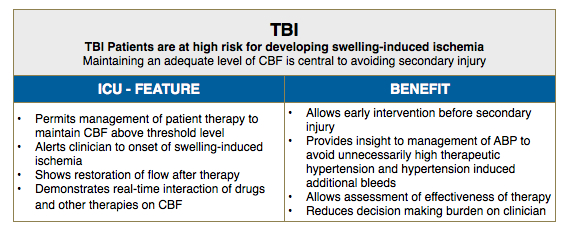
Hemedex’s Bowman Perfusion Monitoring System is primarily used in neurosurgical and neurocritical care applications. The utility of the system for detecting vasospasm and other compromised perfusion when managing patients with traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage is well documented, as noted in the publication section.
Select publications for TBI and SAH includes:
Villa, C. Iacca, A.F. Molinari, C. Giussani, G. Aletti, A. Pesenti, and G. Citerio, “Inhalation versus endovenous sedation in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients: effects on regional cerebral blood flow.,” Critical care medicine, vol. 40, no. 10, pp. 2297-804, Oct. 2012.
G. Rosenthal, R. O. Sanchez-Mejia, N. Phan, J. C. Hemphill, C. Martin, and G. T. Manley, Journal of neurosurgery, vol. 114, no. 1, pp. 62–70, Jan. 2011.
G. Rosenthal, J. C. Hemphill, M. Sorani, C. Martin, D. Morabito, W. D. Obrist, G. T. Manley, and J. C. H. Iii, Critical care medicine, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1917–24, Jun. 2008.
The system has also proved useful in a variety of other applications, including organ transplantation, reconstructive surgery, and oncology. Because adequate perfusion is essential to all tissues, there are many conditions for which monitoring blood perfusion could improve treatment, cost, and ultimately patient outcomes. Clinicians and scientists are exploring the use of the BPM in new markets and clinical applications, some of which is noted in the cited literature.
Select publications for other applications include:
Wan, Jennifer J. MD; Cohen, Mitchell J. MD; Rosenthal, Guy MD; Haitsma, Iain K. MD; Morabito, Diane J. RN, MPH; Derugin, Nikita MA; Knudson, M Margaret MD; Manley, Geoffrey T. MD, Journal of Trauma-Injury Infection & Critical Care, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 353–357, 2009.
Great toe-to-thumb microvascular transplantation after traumatic amputation
M. Buncke, H. J. Buncke, and C. K. Lee, Hand clinics, vol. 23, no. 1. pp. 105–15, Feb-2007.
Thermal Diffusion Probe Analysis of Perfusion Changes in Vascular Occlusions of Rabbit Pedicle Flaps
M.B. Khot, P.K. Maitz, B.R. Phillips, H.F. Bowman, J.J. Pribaz, and D.P.Orgill. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. April 2005.
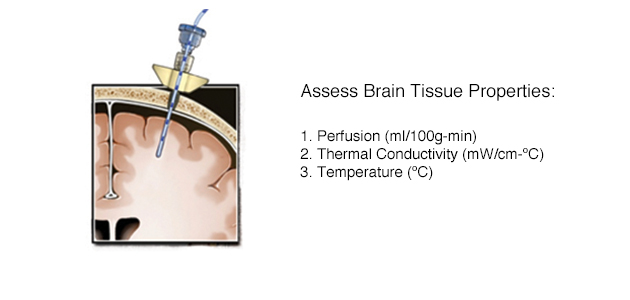
Neurosurgeon/Neurologist/Neurointensivist – Neuro ICU
Integrating Absolute CBF Values with other Brain Physiology: Multimodal Monitoring
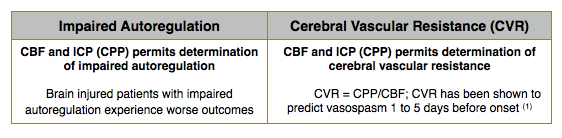
Neurosurgeon OR: Applications of Perfusion (CBF) Monitored in the OR

Additional Features and Benefits Associated with other Parameters:

References:
(1) P. Vajkoczy, P. Horn, C. Thome, E. Munch, and P. Schmiedek, “Regional cerebral blood flow monitoring in the diagnosis of delayed ischemia following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.,” Journal of neurosurgery, vol. 98, no. 6, pp. 1227–34, Jun. 2003.
(2) C. Thomé, P. Vajkoczy, P. Horn, C. Bauhuf, U. Hübner, and P. Schmiedek, “Continuous monitoring of regional cerebral blood flow during temporary arterial occlusion in aneurysm surgery.,” Journal of neurosurgery, vol. 95, no. 3. pp. 402–11, Sep-2001
(3) SB Ko, HA Choi, G Parikh, JM Schmidt, K Lee, N Badjatia, J Claassen, ES Connolly, and SA Mayer, “Real Time Estimation of Brain Water Content in Comatose Patients. “Annuals of Neurology. 72(3):344-50, 2012.