The Power of Knowledge: Transforming Data into Information
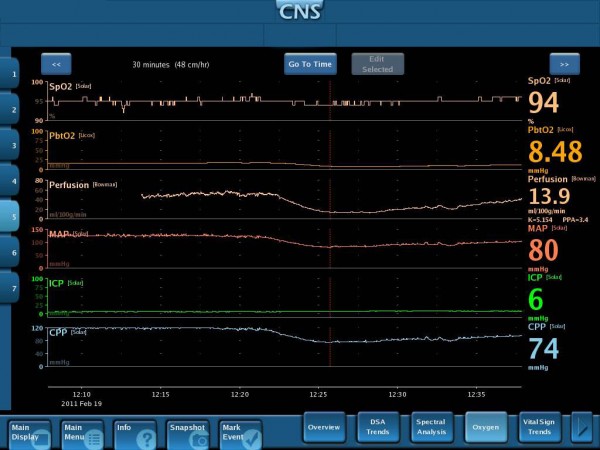
Definition: Multimodal Monitoring is the simultaneous monitoring of multiple physiological parameters to provide context for their interpretation, enhance detection of critical situations, monitor responses to therapeutic interventions and facilitate clinical decision making.
Examples
- Simultaneous interpretation of cerebral perfusion pressure and flow enables detection of impaired autoregulation, a risk factor for poor outcomes
- Simultaneous interpretation of cerebral perfusion pressure and flow enables estimation of cerebral vascular resistance, a predictor of vasospasm1
- Simultaneous interpretation of arterial pressure and cerebral blood flow provides insight into the efficacy of hemodynamic, therapeutic management
Benefits
- The display of multiple parameters in one place facilitates their clinical interpretation
- The combination of parameters provides new features that facilitate clinical management (e.g., cerebral vascular resistance)
- The combination of parameters provides identification of new alarm conditions (e.g., the simultaneous combination of moderately low flow and moderately high blood pressure indicates an untoward state although either condition by itself would not be cause for concern.)
One recommended solution: CNS Systems
References:
(1) Vajkoczy P, et al, Regional cerebral blood flow monitoring in the diagnosis of delayed ischemia following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery (2003) 98:1127-1234.